Top AutoCAD 3D Commands & Shortcuts with Examples
March 13, 2025 2025-04-07 17:02Top AutoCAD 3D Commands & Shortcuts with Examples
Top AutoCAD 3D Commands & Shortcuts with Examples
AutoCAD is one of the most widely used software in engineering and design for creating both 2D and 3D models. When it comes to 3D modeling, mastering AutoCAD 3D commands can significantly enhance your design capabilities, allowing you to create detailed, complex, and accurate models with ease. Whether you’re working on mechanical components, architectural designs, or product prototypes, understanding the right 3D commands can streamline your workflow and improve overall productivity.
In this guide, we’ll explore the 13 essential AutoCAD 3D commands every engineer should master — along with practical examples — to help you elevate your 3D modeling skills. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, these commands will empower you to create professional 3D models with precision and efficiency.
Let’s dive into the world of AutoCAD 3D commands and unlock your design potential!
Basic AutoCAD 3D Commands
1. Extrude
Example
Step 1: Select the rectangle.
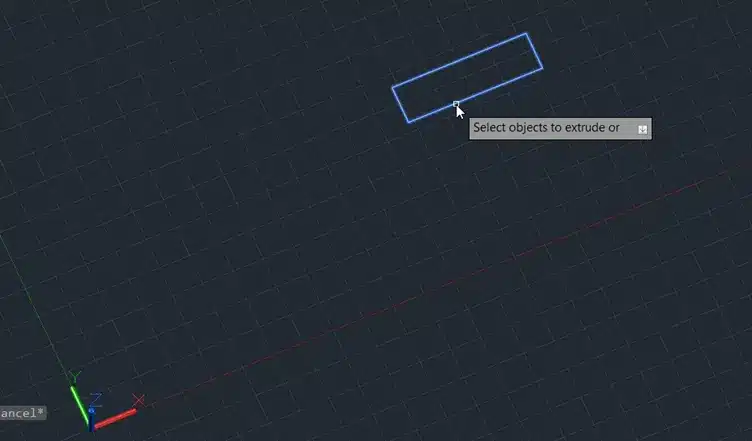
Step 2: Enter the height of extrusion, for example, 1000 unit.
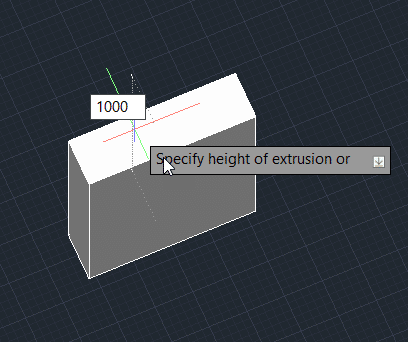
Step 3: Press Enter.
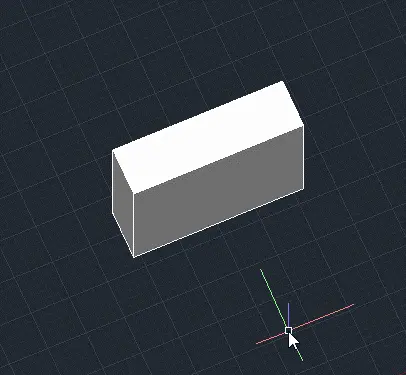
This will create a 3D box with the base as the rectangle and a height of 1000 units.
2. Revolve (REVOLVE)
The REVOLVE command is used to create a 3D solid or surface by revolving a 2D shape around an axis.
Example
Step 1: Draw a profile of a bottle (a half section) on the XY plane.
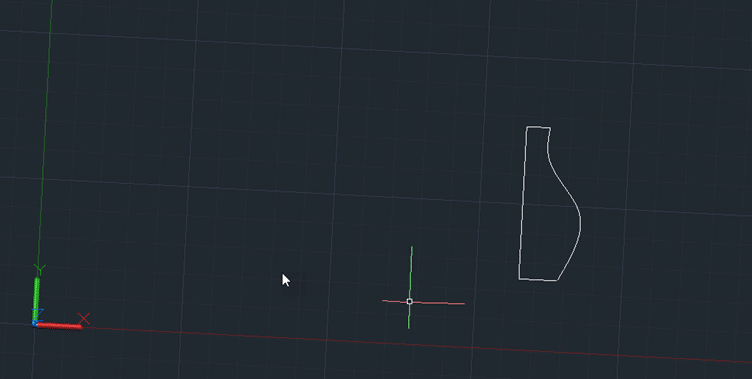
Step 2: Type REVOLVE in the command line and press Enter.
Step 3: Select the profile.
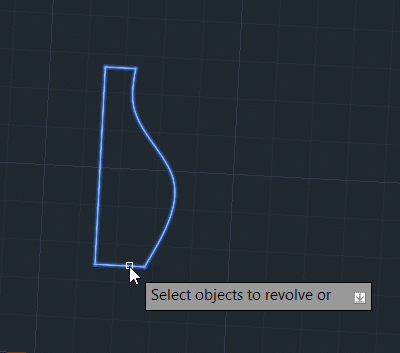
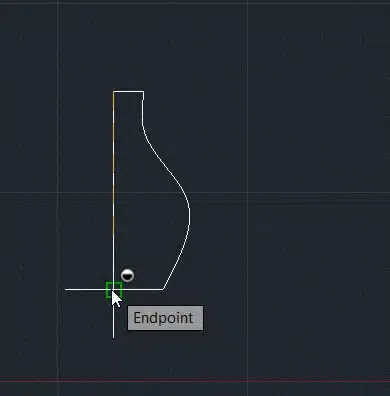
Step 4: Specify the axis of revolution by selecting two points.
Step 5: Enter the angle of revolution, for example, 360 degrees.
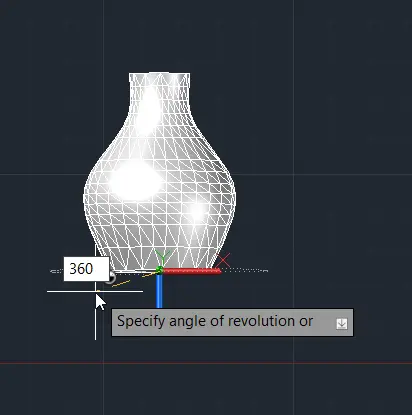
Step 6: Press Enter.
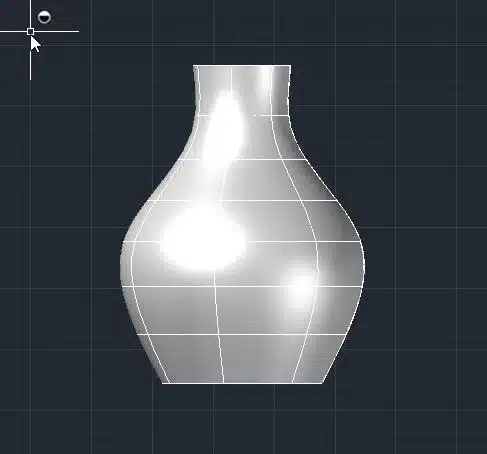

This will create a 3D bottle by revolving the 2D profile around the specified axis.
4. Presspull (PRESSPULL)
The PRESSPULL command is used to create a 3D solid by extruding a face or a closed boundary.
Example
Step 1: Draw a rectangle on the XY plane.
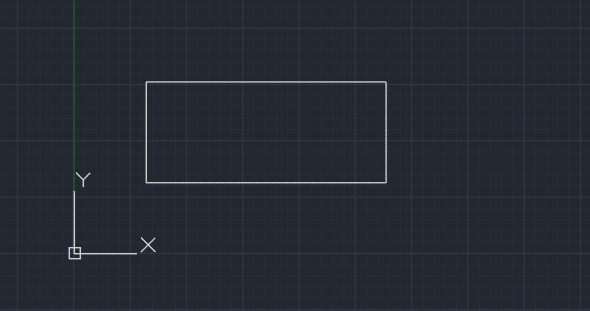
Step 2: Type PRESSPULL in the command line and press Enter
Step 3: Click inside the rectangle.
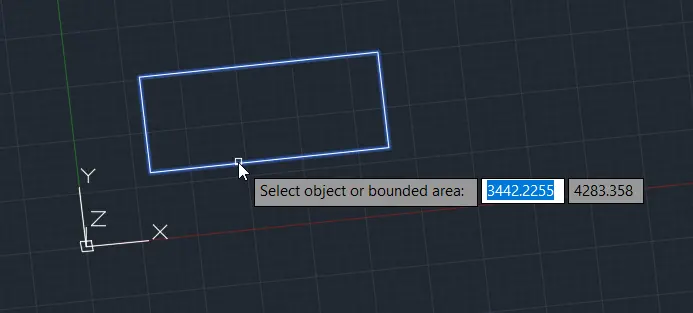
Step 4: Enter the height of extrusion, for example, 1000 units.
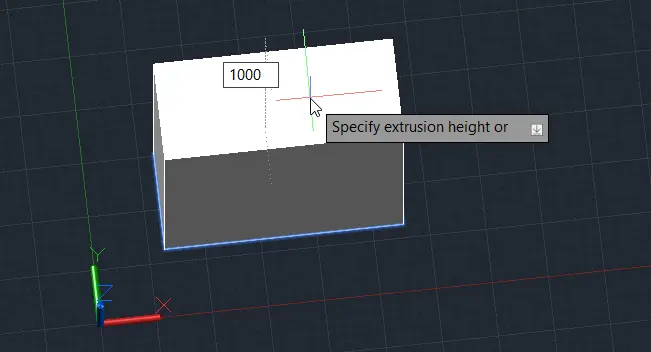
Step 5: Press Enter.
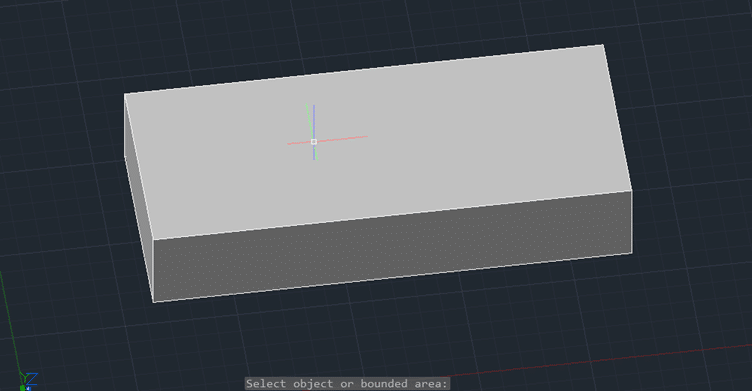
This will create a 3D box similar to the EXTRUDE command.
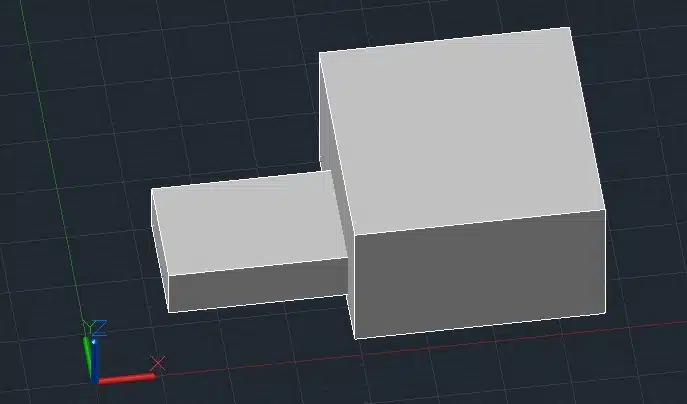
5. Union (UNION)
The UNION command combines two or more 3D solids into one solid.
Example
Step 1: Create two overlapping 3D boxes.
Step 2: Type UNION in the command line and press Enter.
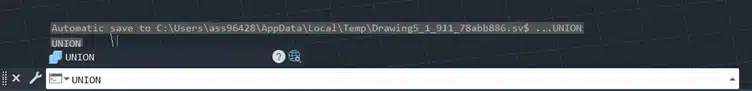
Step 3: Select both boxes.
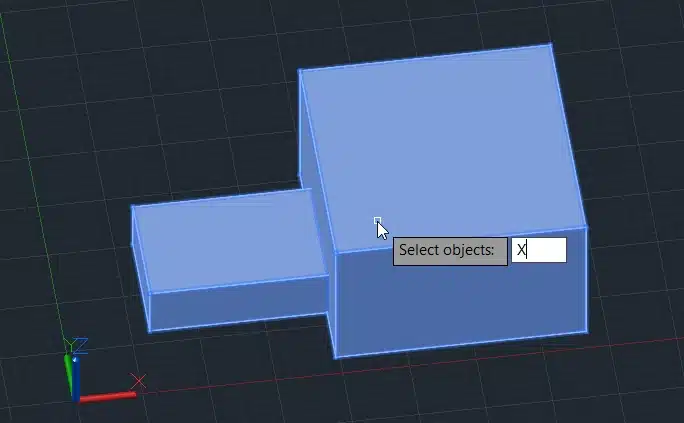
Step 4: Press Enter.
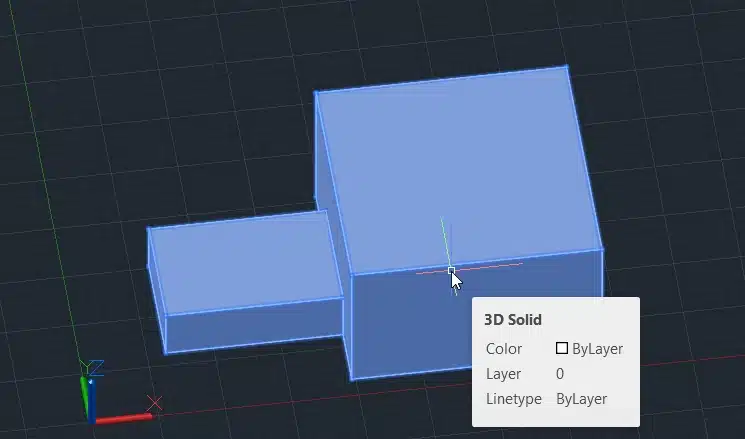
This will combine the two boxes into one single 3D solid.
6. Subtract (SUBTRACT)
The SUBTRACT command removes the volume of one 3D solid from another.
Example
Step 1: Create two overlapping 3D boxes.
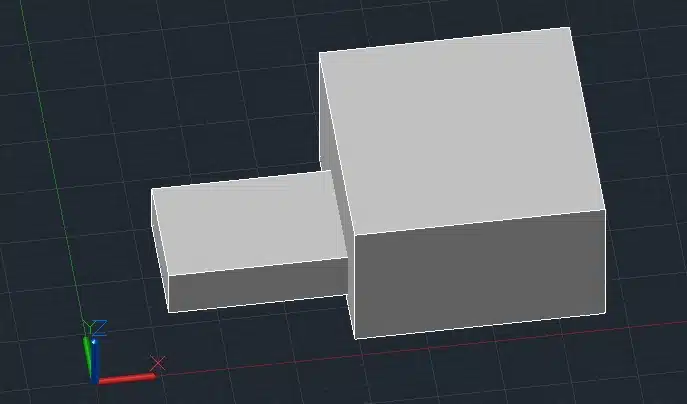
Step 2: Type SUBTRACT in the command line and press Enter.

Step 3: Select the box you want to keep.
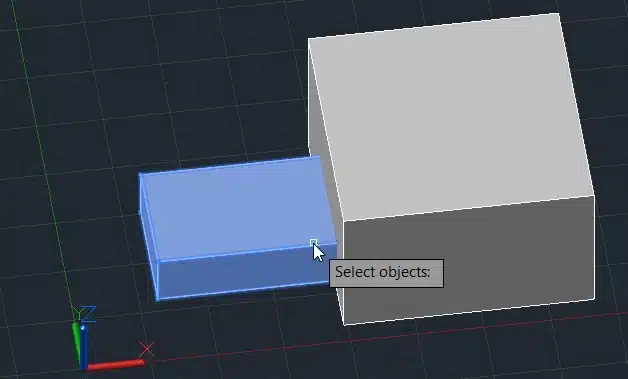
Step 4: Press Enter.
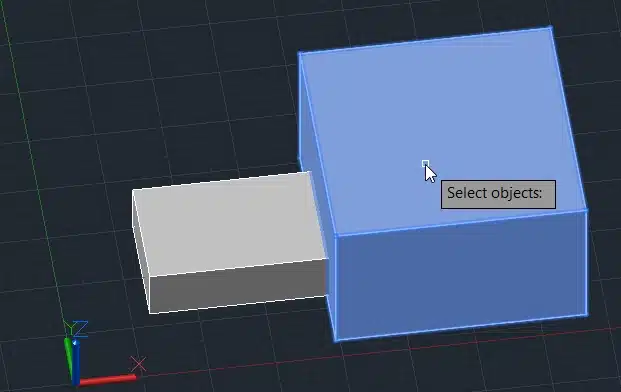
Step 5: Select the box you want to subtract.
Step 6: Press Enter.

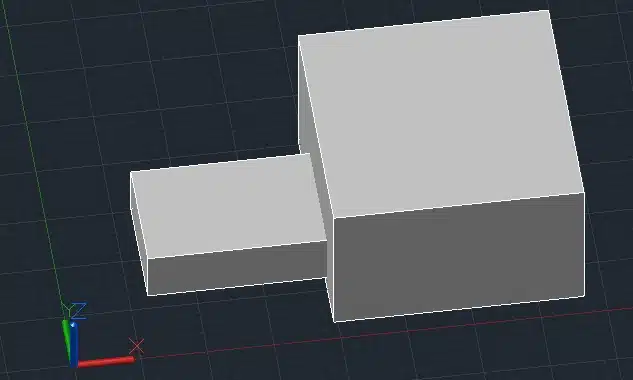
This will subtract the second box from the first box, creating a cutout.
7. Intersect (INTERSECT)
The INTERSECT command creates a 3D solid from the overlapping volume of two or more solids.
Example
Step 1: Create two overlapping 3D boxes.

Step 2: Type INTERSECT in the command line and press Enter.

Step 3: Select both boxes.
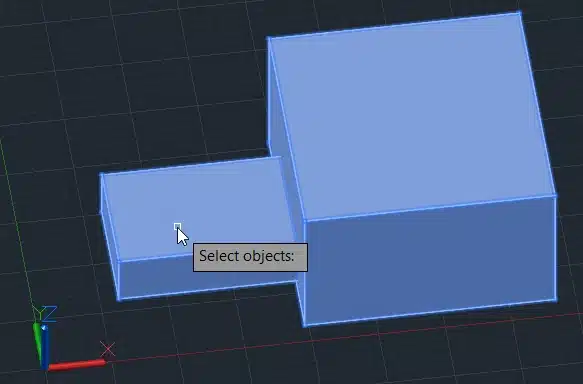
Step 4: Press Enter.
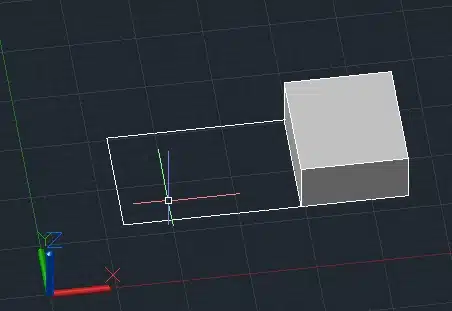
This will create a new 3D solid from the overlapping volume of the two boxes.
📌Also Read: How to Create Stitch Weld in Weldments using Autodesk Inventor?
Advanced AutoCAD 3D Commands
1. Sweep (SWEEP)
The SWEEP command is used to create a 3D solid or surface by sweeping a 2D shape along a specified path.
Example
Step 1: Draw a circle on the XY plane (profile) and a spline (path) on the same or a different plane.
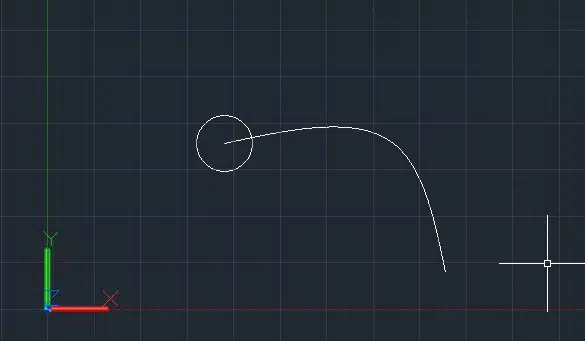
Step 2: Type SWEEP in the command line and press Enter.
Step 3: Select the circle.
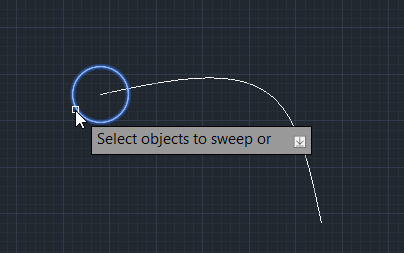
Step 4: Select the spline as the path.
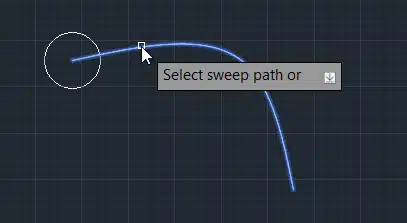
Step 5: Press Enter.

This will create a 3D tube by sweeping the circle along the spline path.
2. Slice (SLICE)
The SLICE command splits a 3D solid or surface into two or more parts.
Example
Step 1: Create a 3D box.
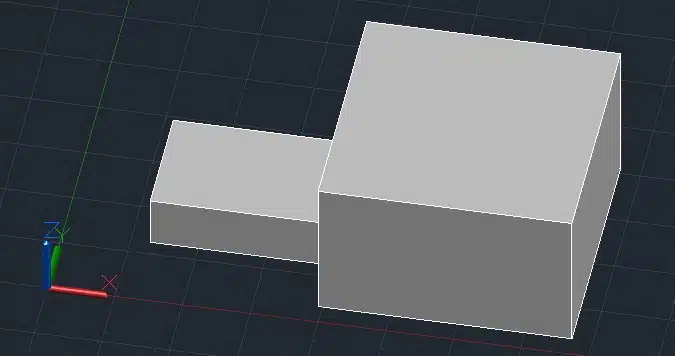
Step 2. Type SLICE in the command line and press Enter.
Step 3. Select the box.
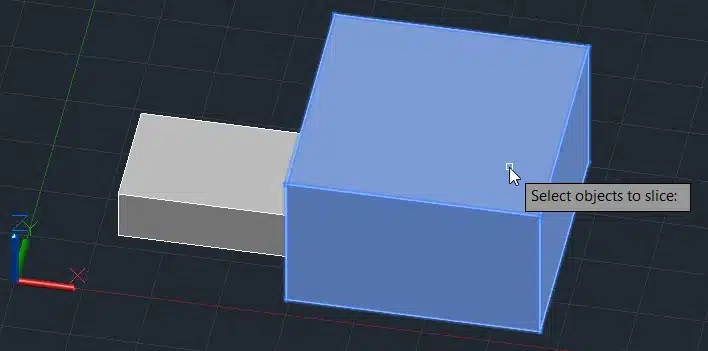
Step 4: Specify the slicing plane by selecting three points.
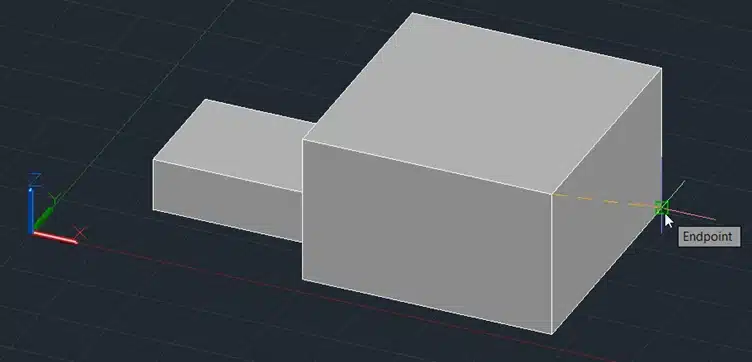
Step 5: Press Enter.
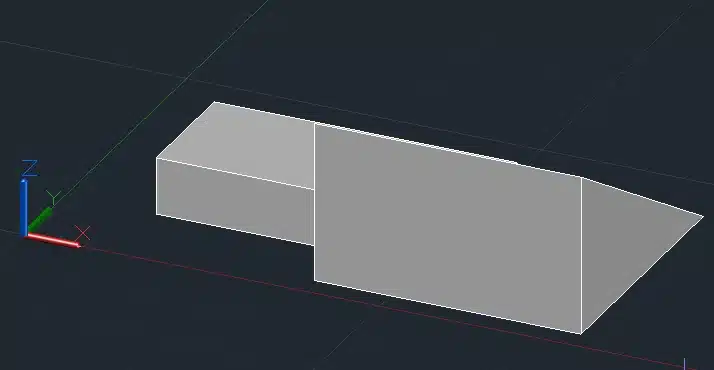
This will split the box into two parts along the specified plane.
3. Fillet (FILLET)
The FILLET command rounds the edges of a 3D solid.
Example
Step 1: Create a 3D box.
Step 2: Type FILLET in the command line and press Enter.
Step 3: Type R and press Enter to specify the fillet radius.

Step 4: Enter the desired radius, for example, 2 units.

Step 5: Select the edge(s) you want to fillet.
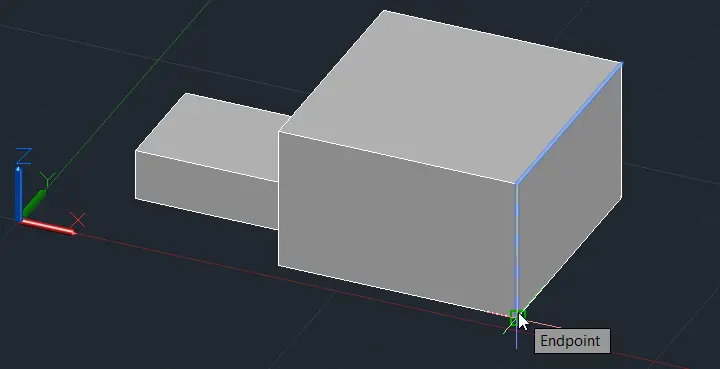
Step 6: Press Enter.
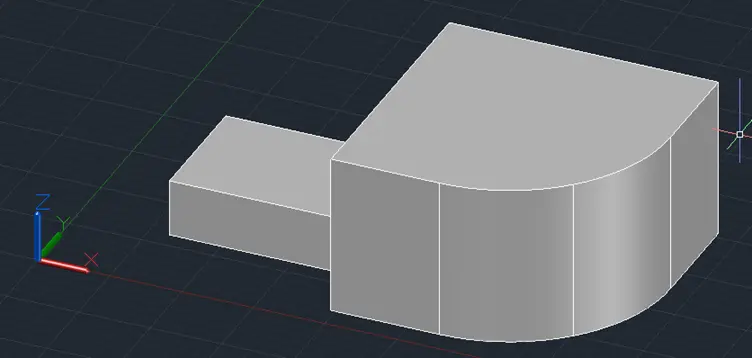
This will round the selected edges of the box with the specified radius.
4. Chamferedge (CHAMFEREDGE)
The CHAMFEREDGE command bevels the edges of a 3D solid.
Example
Step 1: Create a 3D box.

Step 2: Type CHAMFEREDGE in the command line and press Enter.

Step 3: Select edge

Step 4: Enter D the distance

Step 5: Enter distance, for example, 200 units.
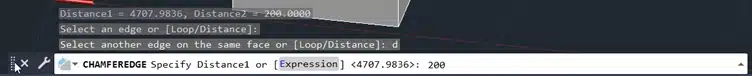
Step 6: Press Enter.
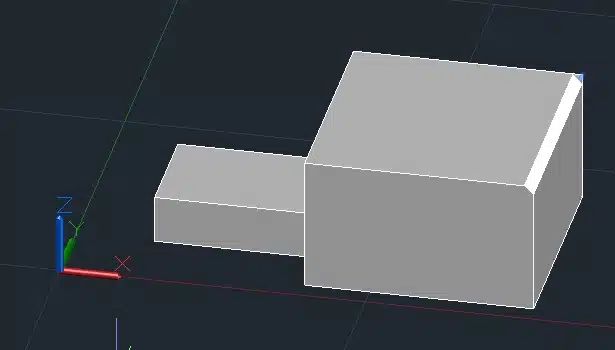
This will bevel the selected edges of the box with the specified distances.
5. Mirror3D (MIRROR3D)
The MIRROR3D command creates a mirrored copy of a 3D object.
Example
Step 1: Create a 3D box.

Step 2: Type MIRROR3D in the command line and press Enter.
Step 3: Select the box.
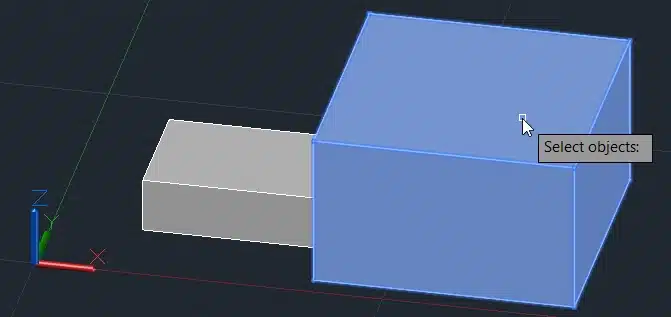
Step 4: Specify the mirroring plane by selecting three points.

Step 5: Press Enter.
This will create a mirrored copy of the box across the specified plane.
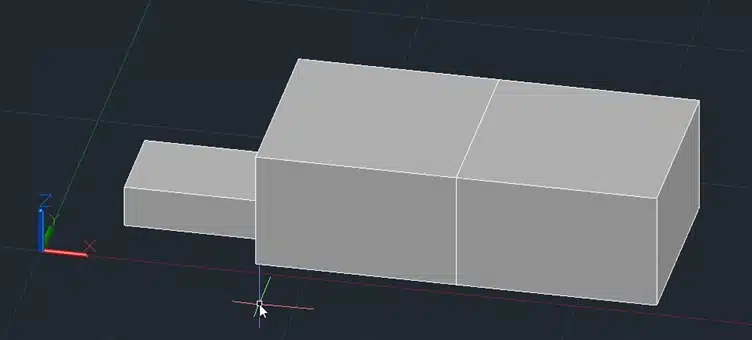
6. Rotate3D (ROTATE3D)
The ROTATE3D command rotates a 3D object around a specified axis.
Example
Step 1: Create a 3D box.
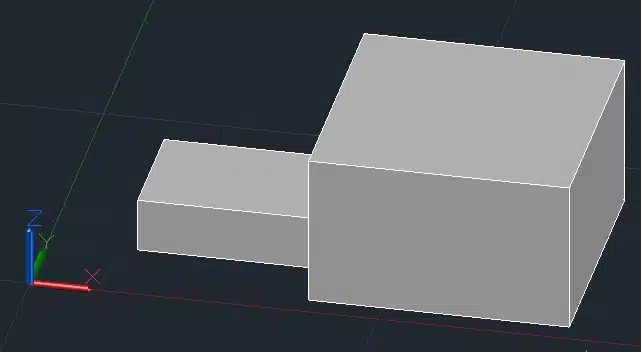
Step 2: Type ROTATE3D in the command line and press Enter.
Step 3: Select the box.
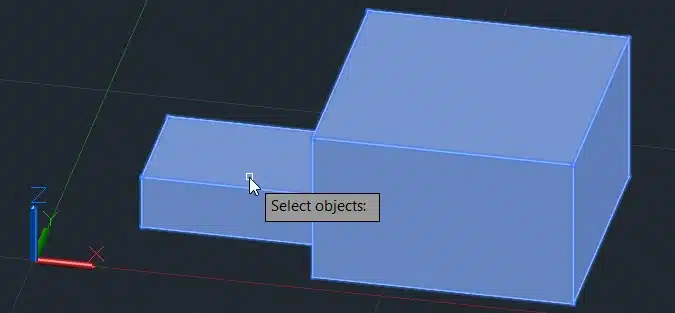
Step 4: Specify the axis of rotation by selecting two points.

Step 5: Enter the angle of rotation, for example, 45 degrees.
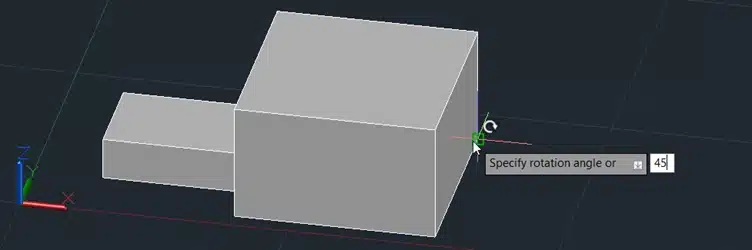
Step 6: Press Enter.
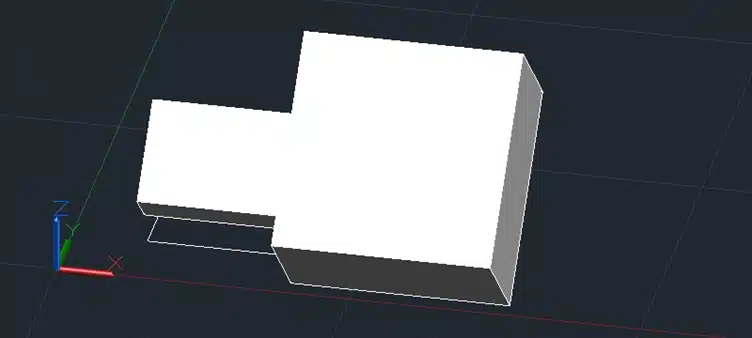
This will rotate the box around the specified axis by the specified angle.
7. Scale3D (SCALE)
The SCALE command scales a 3D object by a specified factor.
Example
Step 1: Create a 3D box.

Step 2: Type SCALE in the command line and press Enter.
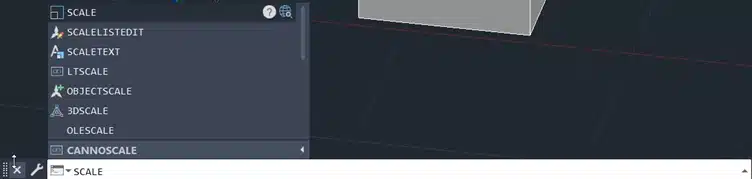
Step 3: Select the box.

Step 4: Specify the base point for scaling.
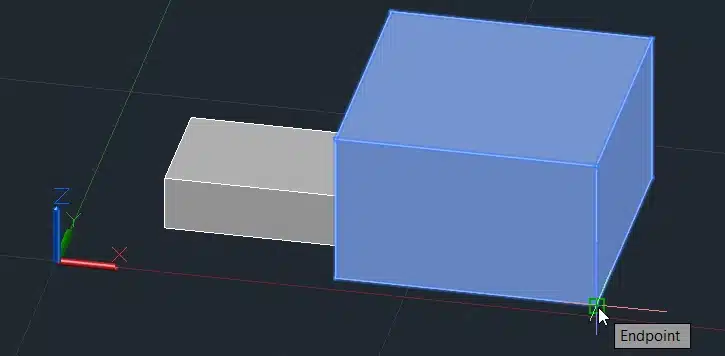
Step 5: Enter the scale factor, for example, 1.5.
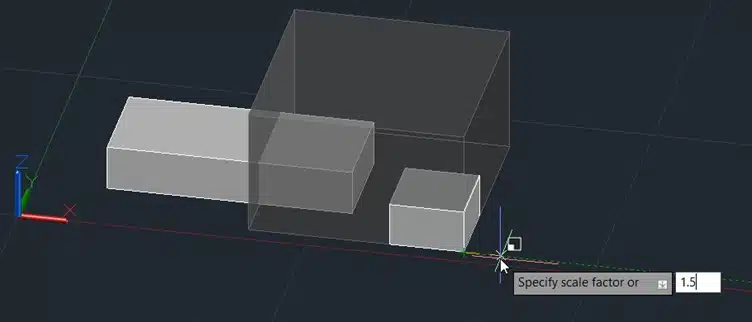
Step 6: Press Enter.

This will scale the box by the specified factor.
8. Align (ALIGN)
The ALIGN command aligns a 3D object with another object in 3D space.
Example
Step 1: Create two 3D boxes.
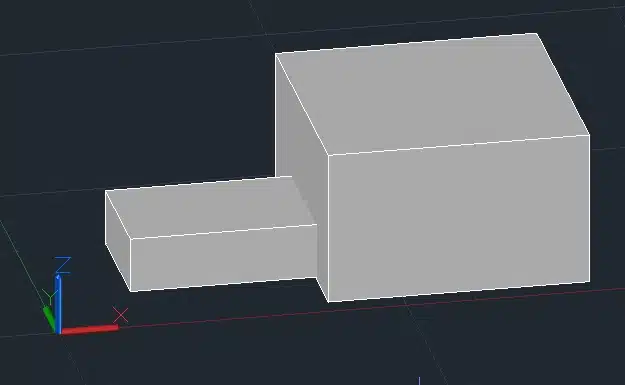
Step 2: Type ALIGN in the command line and press Enter.

Step 3: Select the box you want to align.
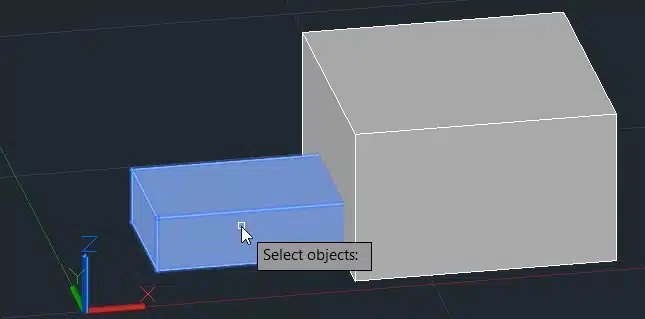
Step 4: Specify the source and destination points to align the objects.
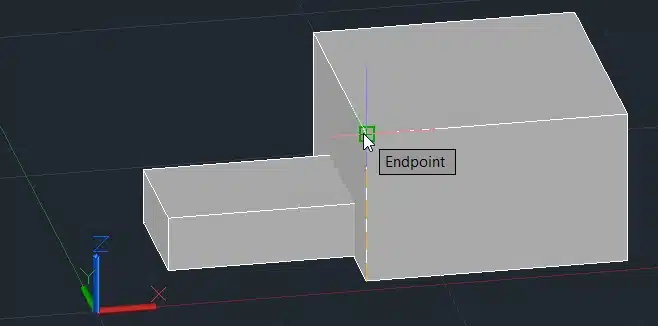
Step 5: Press Enter.
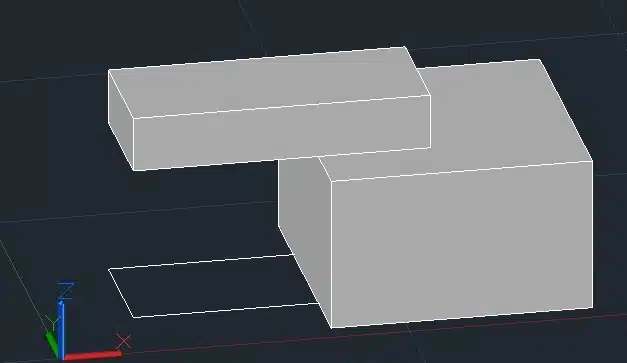
This will align the first box with the second box based on the specified points.
Conclusion
AutoCAD 3D commands are powerful tools that allow you to create complex and detailed 3D models. By mastering these commands, you can enhance your design capabilities and efficiency. This guide provides a starting point, and further exploration and practice will help you become proficient in using AutoCAD for 3D modelling.
Related Posts
How to Create Stitch Weld in Weldments using Autodesk Inventor?
How to Create Blend Curve on Surface using Siemens NX?
How to Enhance Project Sketched Points in Creo Parametric 11.0?
Creating a MultiHole with Simple Hole Type in CATIA V5 R34
The Key Electric Vehicle Components – EV Parts & Its Functions
Find
Categories
Latest Posts
Top AutoCAD 3D Commands & Shortcuts with Examples
March 13, 2025Best EV Online Courses with Certification by Tata Technologies
January 22, 2025Popular Tags









![PLM Teamcenter Interview Questions and Answers – [HR Expert List]](https://igetitv2ww-dev.myigetit.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/blog-350-x-197-px-100x80.webp)








